Eczema is a condition that causes the skin to become inflamed or irritated and is also known as atopic dermatitis. This skin condition normally affects infants and they tend to grow out of it by their 10th birthday but unfortunately 3% of the population have symptoms on and off throughout life. With proper treatment, the disease often can be controlled.
What Are the Symptoms of Eczema?
The most common place for eczema to appear is mainly on the face, back of knees, wrists, hands, or feet and is very itchy. The itchyness may start before the rash. The rash will appear very dry, thickened, or scaly. If you have fair-skinned the affected area may turn brown in appearance but if you have darker-skin, this skin condition may affect their pigmentation and the affected area will turn either lighter or darker.
What Causes Eczema?
Eczema is not contagious and can’t be spread from person to person. Though it is not know what causes eczema but it has been speculated that it may be the body’s overactive immune response to an irritant. It has also been linked to families with a history of other allergies and asthma. There is also a connection to the breakdown of the skin barrier that allows for the lost of moisture and allowing germs in.
Though they may not know what causes eczema there are triggers that will cause eczema to flare up. It can be as simple as coming in contact with rough or coarse surfaces, or the extreme of temperature or come in contact with certain household products mainly soaps and detergent. Some suffers can be triggered by animal dander (similar to human dandruff), certain foods and even the common cold and other upper respiratory infections like colds. Like many other skin conditions stress can cause the condition to worsen.
How Is Eczema Treated?
The first goal when treating eczema is to avoid known triggers. You can have your medical practitioner perform an allergy test to determine possible irritants or triggers.
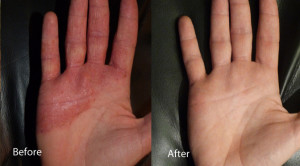
When affected with eczema the priority is to relieve and prevent itching of the infected area. A cold compress can provide relieve from the itchiness with the use of antihistamines. The next step is to help the skin to retain moisture and not allow for bacteria into the skin. The use of a moisturizer regularly will help. The best type of moisturizer is one that help with the prevention of loss of moister from your skin. The best natural ingredients for this is Shea butter, beeswax, jojoba. The Non natural ingredients are Mineral Waxes like paraffin and petrolatum (Vaseline)
Another treatment that can be offered is phototherapy this is where ultraviolet light applied to the skins an effective treatment for moderate to severe eczema if it is carefully controlled and the proper precautions are taken.
If the eczema is more servere then the use of corticosteroids creams and antibiotics may be required to kill infection caused by bacteria. Then there is cyclosporine which is prescribed to suffers that do not respond to all the other treatments.








